Low Voltage Switchgear Systems: Definition, Variations and Areas of Use
In the complex world of electrical engineering, Low Voltage
Switchgear stands as the backbone of safe energy distribution. Whether in a
bustling factory, a high-rise hotel, or a critical hospital, these systems
ensure that power flows reliably, safely, and efficiently.
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the definition,
components, types, and critical standards of low voltage switchgear systems,
helping you make informed decisions for your infrastructure.
What Is Low Voltage Switchgear?
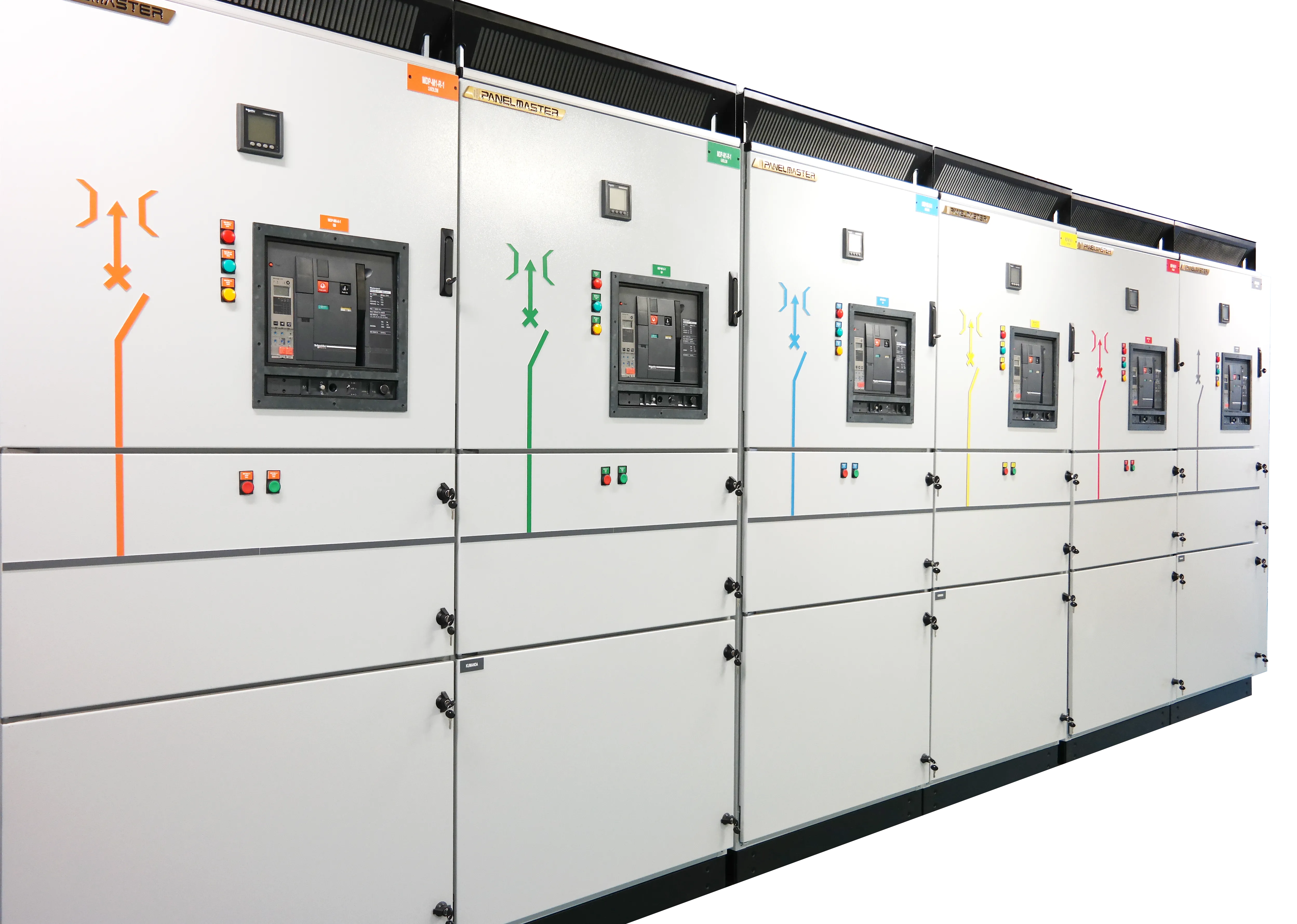
A low voltage switchgear is a protection and control system that safely distributes electrical power across multiple circuits as a definition. As a core component of low voltage power distribution, it includes protective and control devices such as circuit breakers, fuses, busbars, contactors, and measuring equipment. Its main purpose is to ensure safe and reliable operation by preventing failures such as short circuits, overloads, and system disruptions. These safety precautions are vital in the switchgear manufacturing processes. For this reason, a quality system should be preferred.
By definition, a Low Voltage (LV) Switchgear is a
centralized protection and control system designed to safely distribute
electrical power across multiple circuits. It operates as the core component of
low voltage power distribution (typically up to 1000V AC).
It is not just a metal box; it is a sophisticated
assembly containing:
- • Protective devices: Circuit breakers and fuses.
- • Control devices: Contactors and relays.
- • Distribution elements: Busbars and cables.
- • Monitoring equipment: Meters and analyzers.
* Main Purpose: Its primary role
is to ensure safe operation by preventing catastrophic failures such as short
circuits, overloads, and system disruptions. These safety precautions are vital
in the switchgear manufacturing processes.
What Is Low Voltage Switchgear Used For?
Main purposes of using low voltage switchgears:
- Power Distribution: Distribute incoming power to various circuits.
- Protection: Ensure safety against overload and short circuits with circuit breakers and fuses.
- Control: Enable the control of loads such as motors, pumps, and lighting systems.
- Energy efficiency: Help reduce energy consumption to improve reactive power control through compensation systems.
- The utility of switchgear extends beyond simple on/off switching. Its main purposes include:
- 1. Power Distribution: Efficiently distributing incoming power to various subsidiary circuits.
- 2. Protection: safeguarding personnel and equipment against thermal overloads and short circuits.
- 3. Control: Managing the operation of loads such as motors, pumps, and lighting systems.
- 4. Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy consumption and penalties through reactive power control (compensation systems).
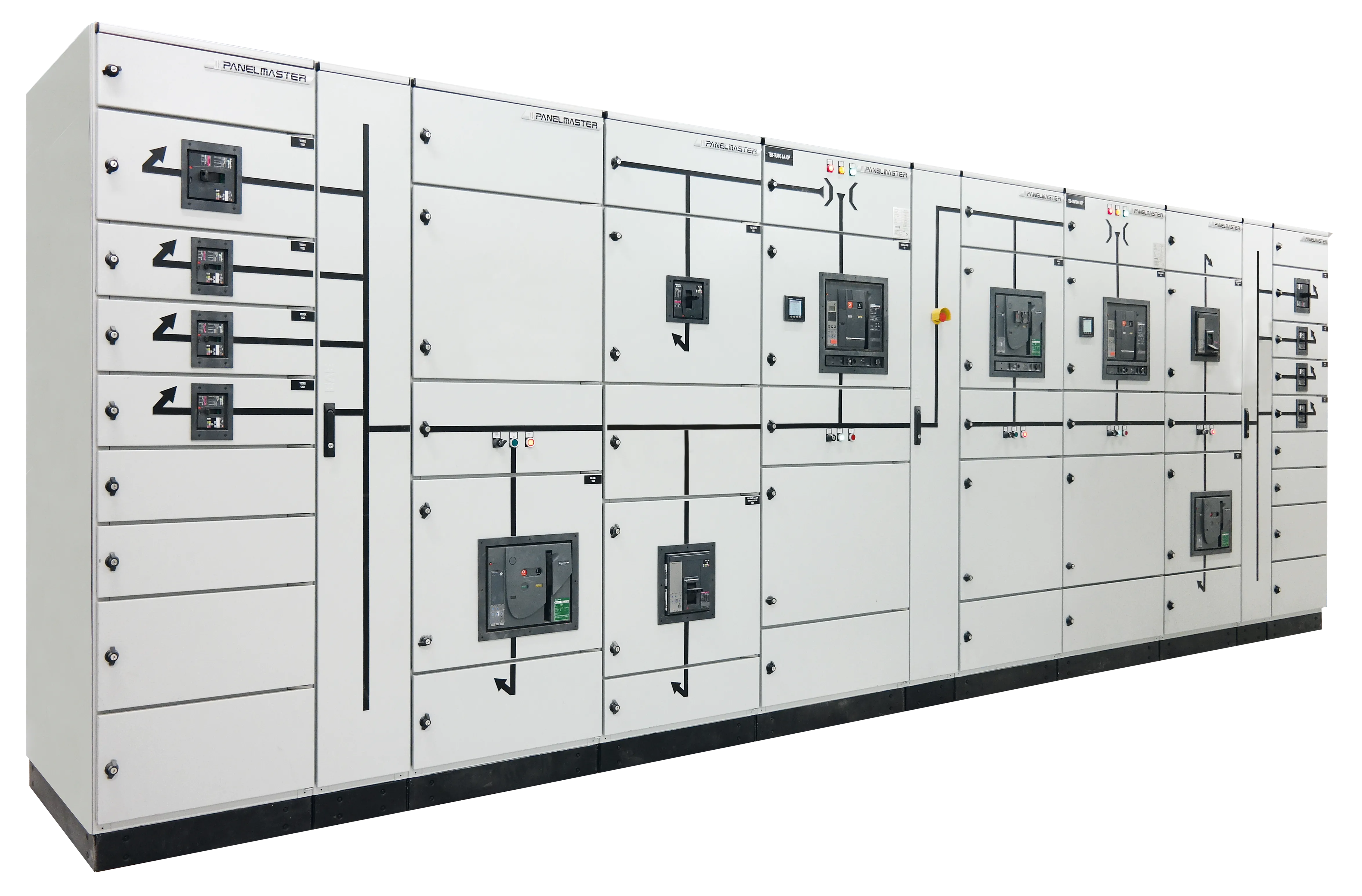
What Are The Types of Low Voltage Switchgears?
They are manufactured in different configurations depending
on their application and function:
LV Switchgears
are manufactured in different configurations depending on their specific
application and function. The most common types include:
1. Power Distribution Board / Main Distribution Board: Manages main incomer power in industrial plants, large commercial buildings, and infrastructure projects.
2. Compensation Panel: Provides reactive power compensation using capacitor banks, helping reduce energy costs and penalties.
3. Automation Panel: Controls processes, machines, and production lines, commonly using PLC and industrial communication modules.
4. Metering Panel: Enables tracking of energy consumption using meters and measurement equipment.
5. Control Panel: Provides start/stop and monitoring control for motors, pumps, conveyors, HVAC systems, and industrial equipment.
6. Fire Safety Panel: Activates emergency systems during fire conditions and plays a critical role in building safety compliance.
1. Main Distribution Board (MDB)
Also known as the Power Distribution Board, this manages the main incomer power in industrial plants, large commercial buildings, and infrastructure projects. It is the first point of entry for power.
2. Compensation Panel
This panel is critical for energy efficiency. It provides reactive power compensation using capacitor banks, helping facilities reduce energy costs and avoid utility penalties.
3. Automation Panel
Designed for “smart” control, these panels manage processes, machines, and production lines, commonly utilizing PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers) and industrial communication modules.
4. Motor Control & Control Panels
These provide start/stop functions and monitoring for motors, conveyors, HVAC systems, and industrial equipment.
5. Fire Safety Panel
A critical safety component that activates emergency systems during fire conditions, playing a vital role in building safety compliance.
6. Metering Panel
Enables precise tracking of energy consumption using advanced meters and measurement equipment.
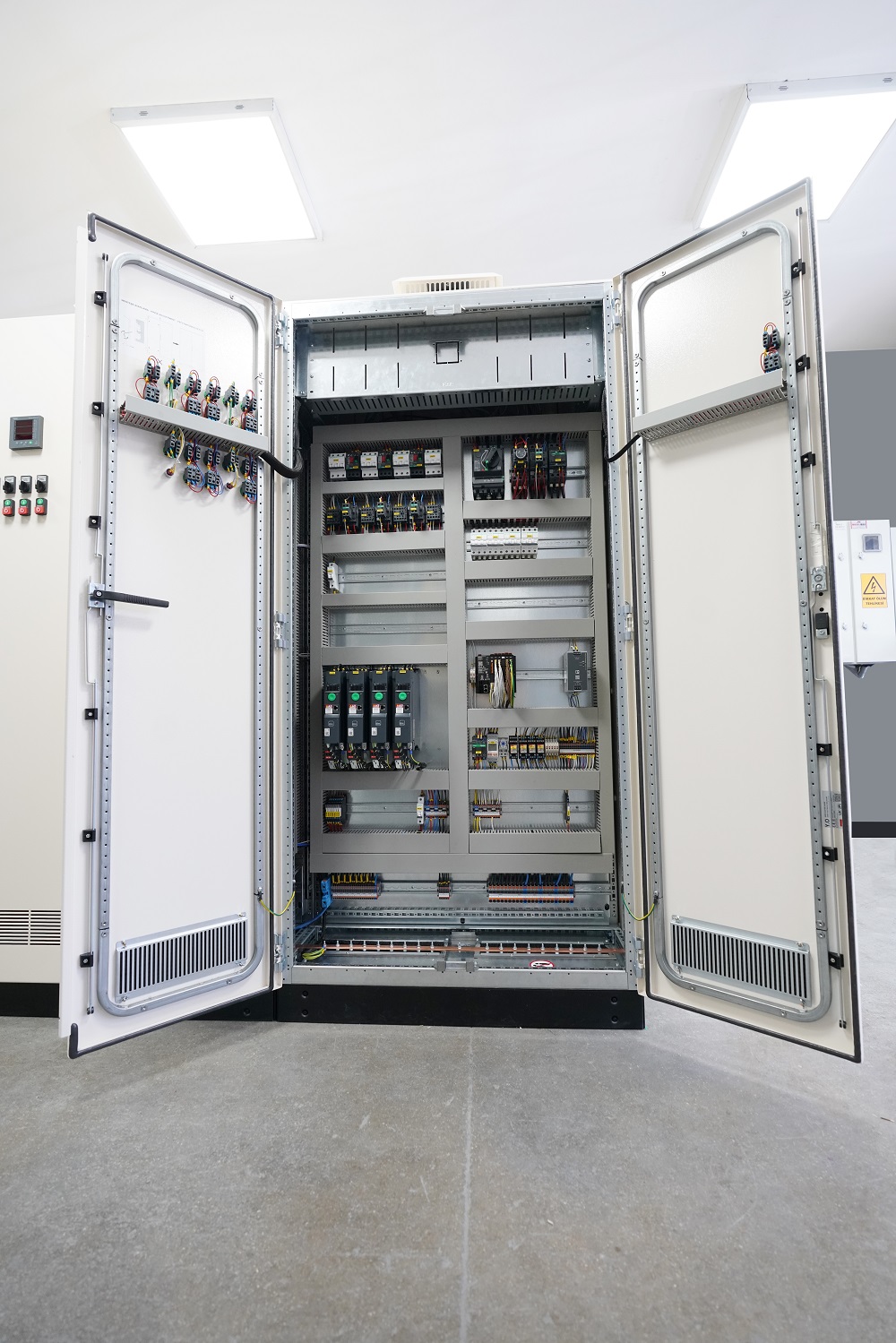
Critical Equipment Inside the Switchgear
Although
the internal structure varies by model, high-quality switchgear typically
includes:
- • Circuit Breakers (ACB/MCCB) & Fuses: The first line of defense against faults.
- • Contactors & Relays: For switching motors and heavy loads.
- • Busbars: Copper or aluminum bars for efficient power distribution within the panel.
- • PLC & Communication Modules: For automation and remote monitoring (SCADA).
- • Power Quality Devices: To monitor harmonics and voltage stability.
Key Considerations for Installation & Assembly
To
ensure longevity and safety, specific factors must be considered during the
design and installation phase:
- • Compliance with Standards: The system must be designed and manufactured according to IEC 61439-1/2, national electrical codes, and occupational health regulations.
- • Insulation and Safety: Live parts must be isolated using insulated materials or grounded metal enclosures to prevent electrical shock.
- • Thermal Management: Switchgears generate heat. Proper temperature rise calculations and ventilation (natural or forced) are essential to prevent overheating.
- • Accurate Labelling: Every device and circuit must be clearly labelled. This simplifies maintenance and eliminates confusion during emergencies.
Where Are The Areas of Use For Low Voltage Switchgears?
Low voltage switchgears are widely used across various
industries and infrastructures, including:
- • Industrial facilities and factories
- • Shopping malls and hotels
- • Commercial and residential buildings
- • Power generation and distribution plants
- • Hospitals and public institutions
What Equipment Is Included In Low Voltage Switchgears?
Although the contents and internal structure of a switchgear
vary by panel models, common equipment includes:
- • Circuit Breakers and Fuses: Protection against short circuits and overloads
- • Contactors and Relays: Motor and load switching
- • Busbars and Cables: Power distribution throughout the panel
- • PLC and Communication Modules: Industrial automation and remote control
- • Meters and Power Quality Devices: Monitoring performance and energy consumption
What Are The Key Considerations in Low Voltage Switchgears Installation/Assembly?
- Compliance
with Standards: A switchgear must be designed and
manufactured according to:
- o IEC 61439-1/2
- o National electrical codes
- o Occupational health and safety regulations
- • Insulation and Safety: Live parts must be safely isolated using insulated materials or grounded metal enclosures to help prevent electrical shock risks.
- • Thermal Management and Ventilation: Switchgears must provide sufficient heat dissipation, including:
- o Proper temperature rise calculations
- o Natural or forced ventilation
- o Scheduled maintenance for cooling components
- • Accurate Labelling: Every device and circuit must be clearly labelled to simplify maintenance and eliminate confusion.
Standards and Regulations : IEC 61439
The system must comply with specific standards to ensure
safety, reliability, and durability:
- • IEC 61439-1/2 (International standard for low voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies)
- • National Electrical Installation Regulations
- • Occupational Health and Safety Legislation
These standards define structural withstand, insulation,
and safety rating. Systems should be designed, manufactured, and type tested in
full compliance with these regulations.
Safety is not optional. A reliable system must comply
with:
- • IEC 61439-1/2: The international standard for low voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies.
- • National Electrical Installation Regulations.
- • Occupational Health and Safety Legislation.
These standards define structural withstand, insulation
properties, and safety ratings. Systems should be fully type-tested to
ensure compliance.
Importance of Periodic Maintenance and Inspections
Routine maintenance of electrical switchgear is essential for
both operational safety and energy efficiency. Periodic inspections help:
- • Prevent overheating and loose connections
- • Detect faults early
- • Ensure continuous and reliable operation

.webp)
.webp)






_shutterstock_750265378.webp)









.webp)




.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
-(1)-(1).webp)


-(1).webp)
-(1).webp)




.webp)
.webp)


.webp)